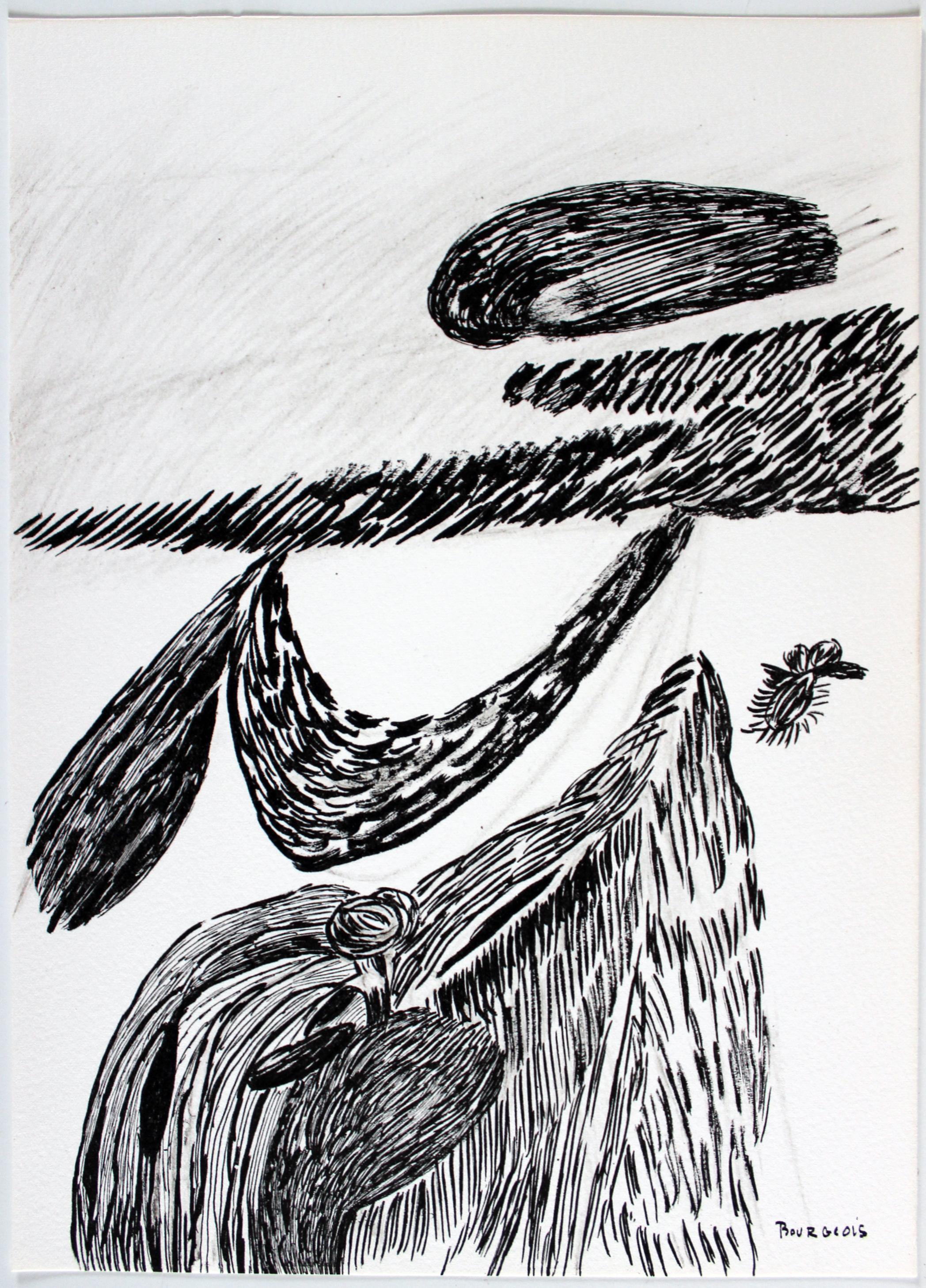
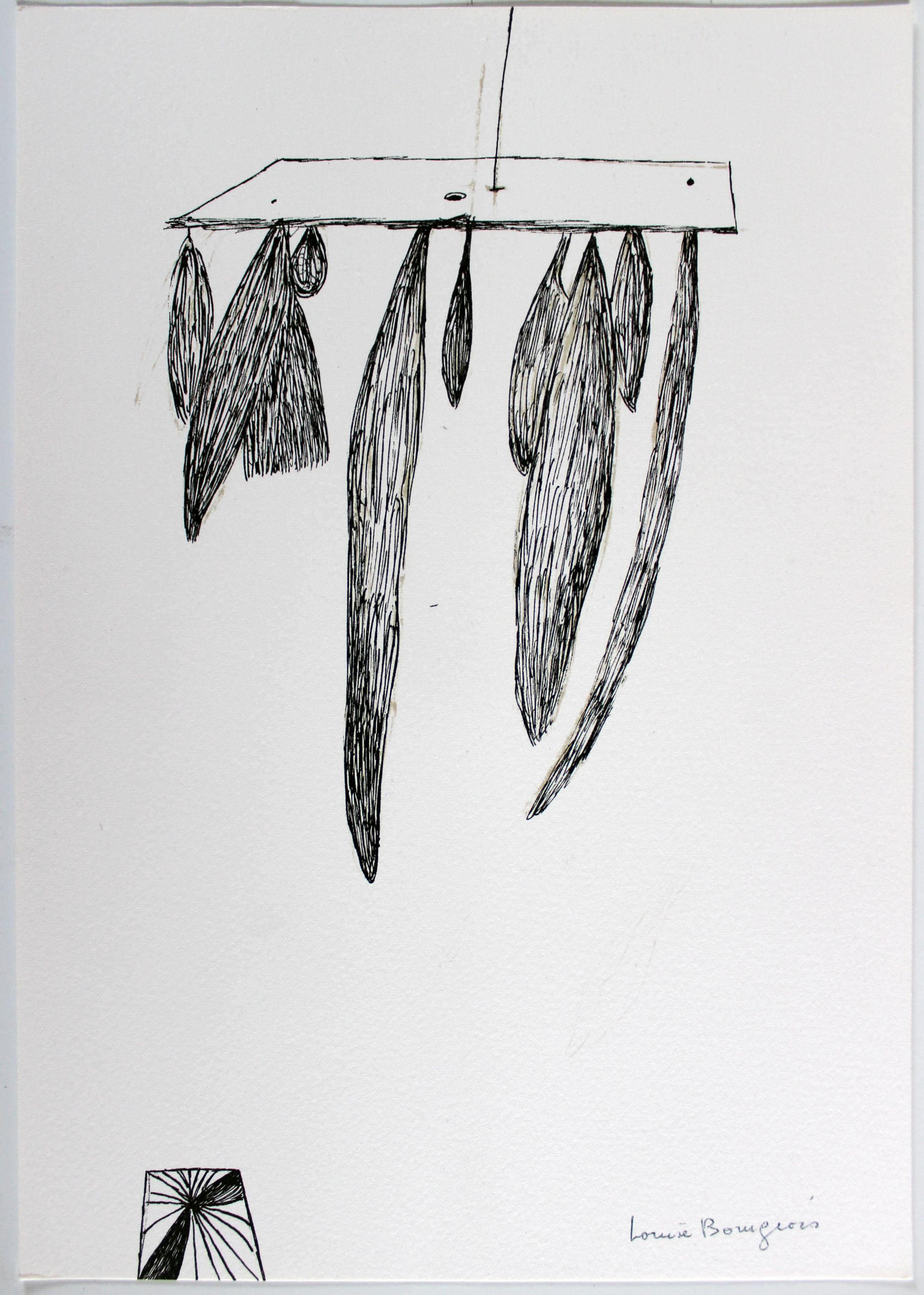
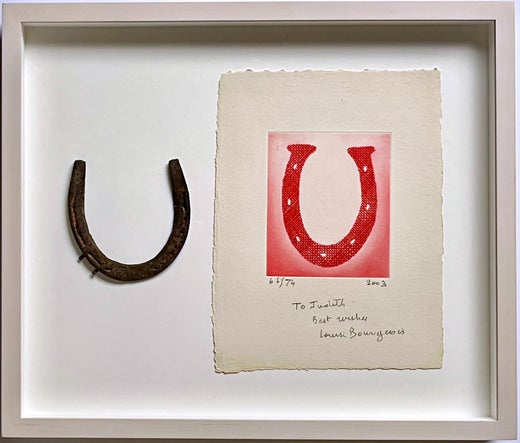
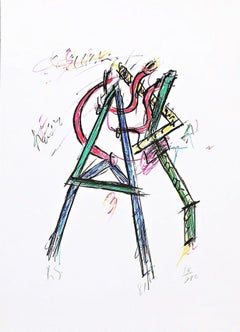Engraving by Louise Bourgeois, 2002, hand signed, numbered and inscribed to her longtime printer Judith Solodkin of Solo Impressions, accompanied by an actual horseshoe gifted by the artist, in a shadowbox frame.
The horseshoe reinforces the image conceptually; is a personal gift from the artist; links to themes of protection, fate, and good luck; the horseshoe is a universal symbol of luck and protection; it is, par excellence, a domestic talisman - and, as such, we believe, will bestow good luck upon the recipient. (The horseshoe is not signed).
Engraving in red, on handmade Nujabi wove paper, 2003, signed, dated and dedicated 'To Judith / Best Wishes / Louise Bourgeois' in pencil, numbered 66/74 (there were also twelve artist's proofs), published by the artist, New York, with full margins, in generally good condition, framed together with a metal horseshoe also given to the printer by the artist
Provenance: Collection of Judith Solodkin, SOLO IMPRESSIONS
Both have been framed together in a museum quality shadow-box style wood frame under UV plexiglass.
Measurements:
Framed:
16 inches (vertical) by 20 inches (horizontal) by 3 inches
Engraving alone:
12.1 inches x 9.25 inches
Literature documenting the engraving: Louise Bourgeois, Deborah Wye (413.2)
Horse Shoe
5 inches by 5 inches
LOUISE BOURGEOIS BIOGRAPHY
b. 1911, Paris; d. 2010, New York
Louise Bourgeois was born on December 25, 1911, in Paris. As a teenager, Bourgeois assisted her parents in their tapestry-restoration business, making drawings that indicated to the weavers the repairs to be made. In 1932 she entered the Sorbonne to study mathematics but abandoned that discipline for art. In the mid- to late 1930s, she studied at the École des beaux-arts, Académie de la grande chaumière, École du Louvre, Atelier Fernand Léger, and other Parisian schools. Bourgeois married the American art historian Robert Goldwater in 1938 and moved to New York. There, she studied for two years at the Art Students League and soon participated in print exhibitions.
After moving to a new apartment in 1941, Bourgeois began to make large wood sculptures on the roof of her building. In 1945 her first solo show, consisting of 12 paintings, was held at the Bertha Schaefer Gallery, New York, and her work was first included in the Whitney Annual (later the Whitney Biennial). In the mid- to late 1940s, she worked at Stanley William Hayter's printshop, Atelier 17, where she met Le Corbusier, Joan Miró, and other Europeans exiled by World War II. In 1949 she exhibited works from her series of Personnages (1945–55) in the first solo show of her sculpture at Peridot Gallery, New York.
Bourgeois became an American citizen in 1951. Continuing her mode of abstracted figuration instilled with psychological and symbolic content, she remained stylistically distinct from New York school developments. She did, however, join American Abstract Artists in 1954. In the 1960s, she taught in public schools and at Brooklyn College and Pratt Institute, Brooklyn. She continued to teach at colleges and universities during the following decade. In the late 1960s, Bourgeois's imagery became more explicitly sexual as she explored the relationship between men and women and the emotional impact of her troubled childhood (her father had had a ten-year affair with her governess). From 1967 until 1972, she made trips to Pietrasanta, Italy, to work in marble.
With the rise of feminism and the art world's new pluralism, her work found a wider audience. In the 1970s, she began to do performance pieces—among them A Banquet/A Fashion Show of Body Parts (1978), in which she wrapped art historians and students in white drapery with sewn-in anatomical forms—and expanded the scale of her three-dimensional work to large environments.
Her first retrospective was organized by the Museum of Modern Art, New York (1982–83), and her first European retrospective was assembled by the Frankfurter Kunstverein, Frankfurt, Germany (1989–91). Bourgeois was selected to be the American representative to the 1993 Venice Biennale. Her collected writings were published in 1998. In 2000, I Do, I Undo, and I Redo—three 30-foot-high towers commissioned by the Tate Modern in London—were featured in the museum's inaugural exhibition. Many of her large-scale works have been exhibited as public art, including three spider sculptures installed at Rockefeller Center in New York in 2001 under the aegis of the Public Art Fund. Major museum retrospectives have since been organized by the Guggenheim Museum Bilbao (2001–02); State Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg (2001–03); and Tate Modern, London (2007–08)—an exhibition that traveled to the Guggenheim Museum (2008).
Bourgeois's achievements have been recognized with a fellowship from the National Endowment for the Arts (1973), membership in the American Academy of Arts and Sciences (1981), a grand prize in sculpture from the French Ministry of Culture (1991), the National Medal of Arts (1997), the Leone d'Oro (1999), a Medal of Honor from the Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts in Philadelphia (2005), the 2006 Intrepid Award from the National Organization for Women (2006), and the Woman Award from the United Nations and Women Together (2007), among others. Bourgeois died on May 31, 2010, in New York.