Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 6
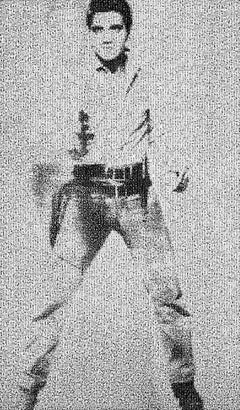
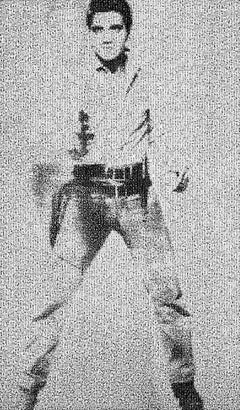
Destro60x40 "Triple Elvis by Warhol" Photomosaic Pop Fine Art Photography Signed2021
2021
$800List Price
About the Item
- Creator:Destro (American)
- Creation Year:2021
- Dimensions:Height: 60 in (152.4 cm)Width: 40 in (101.6 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement Style:
- Period:
- Framing:Framing Options Available
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Los Angeles, CA
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU1130217178112
About the Seller
5.0
Platinum Seller
Premium sellers with a 4.7+ rating and 24-hour response times
1stDibs seller since 2019
638 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 1 hour
Authenticity Guarantee
In the unlikely event there’s an issue with an item’s authenticity, contact us within 1 year for a full refund. DetailsMoney-Back Guarantee
If your item is not as described, is damaged in transit, or does not arrive, contact us within 7 days for a full refund. Details24-Hour Cancellation
You have a 24-hour grace period in which to reconsider your purchase, with no questions asked.Vetted Professional Sellers
Our world-class sellers must adhere to strict standards for service and quality, maintaining the integrity of our listings.Price-Match Guarantee
If you find that a seller listed the same item for a lower price elsewhere, we’ll match it.Trusted Global Delivery
Our best-in-class carrier network provides specialized shipping options worldwide, including custom delivery.You May Also Like
"Triple Elvis" Denied Andy Warhol Silver Black Pop Art Painting by Charles Lutz
By Charles Lutz
Located in Brooklyn, NY
"Triple Elvis" (Denied) Silkscreen Painting by Charles Lutz
Silkscreen and silver enamel paint on canvas with Artist's Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board.
82 x 72" inches
2010
This important example was shown alongside works by Warhol in a two-person show "Warhol Revisited (Charles Lutz / Andy Warhol)" at UAB Abroms-Engel Institute for the Visual Arts in 2024.
Lutz's 2007 ''Warhol Denied'' series gained international attention by calling into question the importance of originality or lack thereof in the work of Andy Warhol. The authentication/denial process of the [[Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board]] was used to create value by submitting recreations of Warhol works for judgment with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED". The final product of the conceptual project being "officially denied" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz.
Based on the full-length Elvis Presley paintings by Pop Artist Andy Warhol in 1964, this is likely one of his most iconic images, next to Campbell's Soup Cans and portraits of Jackie Kennedy, Marilyn Monroe, Liz Taylor, and Marlon Brando. This is the rarest of the Elvis works from the series, as Lutz sourced a vintage roll of 1960's primed artist linen which was used for this one Elvis. The silkscreen, like Warhol's embraced imperfections, like the slight double image printing of the Elvis image.
Lutz received his BFA in Painting and Art History from Pratt Institute and studied Human Dissection and Anatomy at Columbia University, New York. Lutz's work deals with perceptions and value structures, specifically the idea of the transference of values. Lutz's most recently presented an installation of new sculptures dealing with consumerism at Frank Lloyd Wright's Fallingwater House in 2022.
Lutz's 2007 Warhol Denied series received international attention calling into question the importance of originality in a work of art. The valuation process (authentication or denial) of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board was used by the artist to create value by submitting recreations of Warhol works for judgment, with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED" of their authenticity. The final product of this conceptual project is "Officially DENIED" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz.
Later in 2013, Lutz went on to do one of his largest public installations to date. At the 100th Anniversary of Marcel Duchamp's groundbreaking and controversial Armory Show, Lutz was asked by the curator of Armory Focus: USA and former Director of The Andy Warhol Museum, Eric Shiner to create a site-specific installation representing the US. The installation "Babel" (based on Pieter Bruegel's famous painting) consisted of 1500 cardboard replicas of Warhol's Brillo Box (Stockholm Type) stacked 20 ft tall. All 1500 boxes were then given to the public freely, debasing the Brillo Box as an art commodity by removing its value, in addition to debasing its willing consumers.
Elvis was "the greatest cultural force in the Twentieth Century. He introduced the beat to everything, and he changed everything - music, language, clothes, it's a whole new social revolution." Leonard Bernstein in: Exh. Cat., Boston, The Institute of Contemporary Art and traveling, Elvis + Marilyn 2 x Immortal, 1994-97, p. 9.
Andy Warhol "quite simply changed how we all see the world around us." Kynaston McShine in: Exh. Cat., New York, Museum of Modern Art (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 1996, p. 13.
In the summer of 1963 Elvis Presley was just twenty-eight years old but already a legend of his time. During the preceding seven years - since Heartbreak Hotel became the biggest-selling record of 1956 - he had recorded seventeen number-one singles and seven number-one albums; starred in eleven films, countless national TV appearances, tours, and live performances; earned tens of millions of dollars; and was instantly recognized across the globe. The undisputed King of Rock and Roll, Elvis was the biggest star alive: a cultural phenomenon of mythic proportions apparently no longer confined to the man alone. As the eminent composer Leonard Bernstein put it, Elvis was "the greatest cultural force in the Twentieth Century. He introduced the beat to everything, and he changed everything - music, language, clothes, it's a whole new social revolution." (Exh. Cat., Boston, The Institute of Contemporary Art (and traveling), Elvis + Marilyn 2 x Immortal, 1994, p. 9).
In the summer of 1963 Andy Warhol was thirty-four years old and transforming the parameters of visual culture in America. The focus of his signature silkscreen was leveled at subjects he brilliantly perceived as the most important concerns of day to day contemporary life. By appropriating the visual vernacular of consumer culture and multiplying readymade images gleaned from newspapers, magazines and advertising, he turned a mirror onto the contradictions behind quotidian existence. Above all else he was obsessed with themes of celebrity and death, executing intensely multifaceted and complex works in series that continue to resound with universal relevance. His unprecedented practice re-presented how society viewed itself, simultaneously reinforcing and radically undermining the collective psychology of popular culture. He epitomized the tide of change that swept through the 1960s and, as Kynaston McShine has concisely stated, "He quite simply changed how we all see the world around us." (Exh. Cat., New York, Museum of Modern Art (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 1996, p. 13).
Thus in the summer of 1963 there could not have been a more perfect alignment of artist and subject than Warhol and Elvis. Perhaps the most famous depiction of the biggest superstar by the original superstar artist, Double Elvis is a historic paradigm of Pop Art from a breath-taking moment in Art History. With devastating immediacy and efficiency, Warhol's canvas seduces our view with a stunning aesthetic and confronts our experience with a sophisticated array of thematic content. Not only is there all of Elvis, man and legend, but we are also presented with the specter of death, staring at us down the barrel of a gun; and the lone cowboy, confronting the great frontier and the American dream. The spray painted silver screen denotes the glamour and glory of cinema, the artificiality of fantasy, and the idea of a mirror that reveals our own reality back to us. At the same time, Warhol's replication of Elvis' image as a double stands as metaphor for the means and effects of mass-media and its inherent potential to manipulate and condition. These thematic strata function in simultaneous concert to deliver a work of phenomenal conceptual brilliance. The portrait of a man, the portrait of a country, and the portrait of a time, Double Elvis is an indisputable icon for our age.
The source image was a publicity still for the movie Flaming Star, starring Presley as the character Pacer Burton and directed by Don Siegel in 1960. The film was originally intended as a vehicle for Marlon Brando and produced by David Weisbart, who had made James Dean's Rebel Without a Cause in 1955. It was the first of two Twentieth Century Fox productions Presley was contracted to by his manager Colonel Tom Parker, determined to make the singer a movie star. For the compulsive movie-fan Warhol, the sheer power of Elvis wielding a revolver as the reluctant gunslinger presented the zenith of subject matter: ultimate celebrity invested with the ultimate power to issue death. Warhol's Elvis is physically larger than life and wears the expression that catapulted him into a million hearts: inexplicably and all at once fearful and resolute; vulnerable and predatory; innocent and explicit. It is the look of David Halberstam's observation that "Elvis Presley was an American original, the rebel as mother's boy, alternately sweet and sullen, ready on demand to be either respectable or rebellious." (Exh. Cat., Boston, Op. Cit.). Indeed, amidst Warhol's art there is only one other subject whose character so ethereally defies categorization and who so acutely conflated total fame with the inevitability of mortality. In Warhol's work, only Elvis and Marilyn harness a pictorial magnetism of mythic proportions.
With Marilyn Monroe, whom Warhol depicted immediately after her premature death in August 1962, he discovered a memento mori to unite the obsessions driving his career: glamour, beauty, fame, and death. As a star of the silver screen and the definitive international sex symbol, Marilyn epitomized the unattainable essence of superstardom that Warhol craved. Just as there was no question in 1963, there remains still none today that the male equivalent to Marilyn is Elvis. However, despite his famous 1968 adage, "If you want to know all about Andy Warhol, just look at the surface of my paintings" Warhol's fascination held purpose far beyond mere idolization. As Rainer Crone explained in 1970, Warhol was interested in movie stars above all else because they were "people who could justifiably be seen as the nearest thing to representatives of mass culture." (Rainer Crone, Andy Warhol, New York, 1970, p. 22). Warhol was singularly drawn to the idols of Elvis and Marilyn, as he was to Marlon Brando and Liz Taylor, because he implicitly understood the concurrence between the projection of their image and the projection of their brand. Some years after the present work he wrote, "In the early days of film, fans used to idolize a whole star - they would take one star and love everything about that star...So you should always have a product that's not just 'you.' An actress should count up her plays and movies and a model should count up her photographs and a writer should count up his words and an artist should count up his pictures so you always know exactly what you're worth, and you don't get stuck thinking your product is you and your fame, and your aura." (Andy Warhol, The Philosophy of Andy Warhol (From A to B and Back Again), San Diego, New York and London, 1977, p. 86).
The film stars of the late 1950s and early 1960s that most obsessed Warhol embodied tectonic shifts in wider cultural and societal values. In 1971 John Coplans argued that Warhol was transfixed by the subject of Elvis, and to a lesser degree by Marlon Brando and James Dean, because they were "authentically creative, and not merely products of Hollywood's fantasy or commercialism. All three had originative lives, and therefore are strong personalities; all three raised - at one level or another - important questions as to the quality of life in America and the nature of its freedoms. Implicit in their attitude is a condemnation of society and its ways; they project an image of the necessity for the individual to search for his own future, not passively, but aggressively, with commitment and passion." (John Coplans, "Andy Warhol and Elvis Presley," Studio International, vol. 181, no. 930, February 1971, pp. 51-52). However, while Warhol unquestionably adored these idols as transformative heralds, the suggestion that his paintings of Elvis...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Figurative Paintings
Materials
Enamel
$110,000
H 82 in W 72 in D 1 in
"Elvis", Denied Andy Warhol Silver
Black Pop Art Painting by Charles Lutz
By Charles Lutz
Located in Brooklyn, NY
Elvis, Metallic Silver and Black Full Length Silkscreen Painting by Charles Lutz
Silkscreen and silver enamel painted on vintage 1960's era linen with Artist's Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board.
82" x 40" inches
2010
Lutz's 2007 ''Warhol Denied'' series gained international attention by calling into question the importance of originality or lack thereof in the work of Andy Warhol. The authentication/denial process of the [[Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board]] was used to create value by submitting recreations of Warhol works for judgment with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED". The final product of the conceptual project being "officially denied" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz.
Based on the full-length Elvis Presley paintings by Pop Artist Andy Warhol in 1964, this is likely one of his most iconic images, next to Campbell's Soup Cans and portraits of Jackie Kennedy, Marilyn Monroe, Liz Taylor, and Marlon Brando. This is the rarest of the Elvis works from the series, as Lutz sourced a vintage roll of 1960's primed artist linen which was used for this one Elvis. The silkscreen, like Warhol's embraced imperfections, like the slight double image printing of the Elvis image.
Lutz received his BFA in Painting and Art History from Pratt Institute and studied Human Dissection and Anatomy at Columbia University, New York. Lutz's work deals with perceptions and value structures, specifically the idea of the transference of values. Lutz's most recently presented an installation of new sculptures dealing with consumerism at Frank Lloyd Wright's Fallingwater House in 2022.
Lutz's 2007 Warhol Denied series received international attention calling into question the importance of originality in a work of art. The valuation process (authentication or denial) of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board was used by the artist to create value by submitting recreations of Warhol works for judgment, with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED" of their authenticity. The final product of this conceptual project is "Officially DENIED" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz.
Later in 2013, Lutz went on to do one of his largest public installations to date. At the 100th Anniversary of Marcel Duchamp's groundbreaking and controversial Armory Show, Lutz was asked by the curator of Armory Focus: USA and former Director of The Andy Warhol Museum, Eric Shiner to create a site-specific installation representing the US. The installation "Babel" (based on Pieter Bruegel's famous painting) consisted of 1500 cardboard replicas of Warhol's Brillo Box (Stockholm Type) stacked 20 ft tall. All 1500 boxes were then given to the public freely, debasing the Brillo Box as an art commodity by removing its value, in addition to debasing its willing consumers.
Elvis was "the greatest cultural force in the Twentieth Century. He introduced the beat to everything, and he changed everything - music, language, clothes, it's a whole new social revolution." Leonard Bernstein in: Exh. Cat., Boston, The Institute of Contemporary Art and traveling, Elvis + Marilyn 2 x Immortal, 1994-97, p. 9.
Andy Warhol "quite simply changed how we all see the world around us." Kynaston McShine in: Exh. Cat., New York, Museum of Modern Art (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 1996, p. 13.
In the summer of 1963 Elvis Presley was just twenty-eight years old but already a legend of his time. During the preceding seven years - since Heartbreak Hotel became the biggest-selling record of 1956 - he had recorded seventeen number-one singles and seven number-one albums; starred in eleven films, countless national TV appearances, tours, and live performances; earned tens of millions of dollars; and was instantly recognized across the globe. The undisputed King of Rock and Roll, Elvis was the biggest star alive: a cultural phenomenon of mythic proportions apparently no longer confined to the man alone. As the eminent composer Leonard Bernstein put it, Elvis was "the greatest cultural force in the Twentieth Century. He introduced the beat to everything, and he changed everything - music, language, clothes, it's a whole new social revolution." (Exh. Cat., Boston, The Institute of Contemporary Art (and traveling), Elvis + Marilyn 2 x Immortal, 1994, p. 9).
In the summer of 1963 Andy Warhol was thirty-four years old and transforming the parameters of visual culture in America. The focus of his signature silkscreen was leveled at subjects he brilliantly perceived as the most important concerns of day to day contemporary life. By appropriating the visual vernacular of consumer culture and multiplying readymade images gleaned from newspapers, magazines and advertising, he turned a mirror onto the contradictions behind quotidian existence. Above all else he was obsessed with themes of celebrity and death, executing intensely multifaceted and complex works in series that continue to resound with universal relevance. His unprecedented practice re-presented how society viewed itself, simultaneously reinforcing and radically undermining the collective psychology of popular culture. He epitomized the tide of change that swept through the 1960s and, as Kynaston McShine has concisely stated, "He quite simply changed how we all see the world around us." (Exh. Cat., New York, Museum of Modern Art (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 1996, p. 13).
Thus in the summer of 1963 there could not have been a more perfect alignment of artist and subject than Warhol and Elvis. Perhaps the most famous depiction of the biggest superstar by the original superstar artist, Double Elvis is a historic paradigm of Pop Art from a breath-taking moment in Art History. With devastating immediacy and efficiency, Warhol's canvas seduces our view with a stunning aesthetic and confronts our experience with a sophisticated array of thematic content. Not only is there all of Elvis, man and legend, but we are also presented with the specter of death, staring at us down the barrel of a gun; and the lone cowboy, confronting the great frontier and the American dream. The spray painted silver screen denotes the glamour and glory of cinema, the artificiality of fantasy, and the idea of a mirror that reveals our own reality back to us. At the same time, Warhol's replication of Elvis' image as a double stands as metaphor for the means and effects of mass-media and its inherent potential to manipulate and condition. These thematic strata function in simultaneous concert to deliver a work of phenomenal conceptual brilliance. The portrait of a man, the portrait of a country, and the portrait of a time, Double Elvis is an indisputable icon for our age.
The source image was a publicity still for the movie Flaming Star, starring Presley as the character Pacer Burton and directed by Don Siegel in 1960. The film was originally intended as a vehicle for Marlon Brando and produced by David Weisbart, who had made James Dean's Rebel Without a Cause in 1955. It was the first of two Twentieth Century Fox productions Presley was contracted to by his manager Colonel Tom Parker, determined to make the singer a movie star. For the compulsive movie-fan Warhol, the sheer power of Elvis wielding a revolver as the reluctant gunslinger presented the zenith of subject matter: ultimate celebrity invested with the ultimate power to issue death. Warhol's Elvis is physically larger than life and wears the expression that catapulted him into a million hearts: inexplicably and all at once fearful and resolute; vulnerable and predatory; innocent and explicit. It is the look of David Halberstam's observation that "Elvis Presley was an American original, the rebel as mother's boy, alternately sweet and sullen, ready on demand to be either respectable or rebellious." (Exh. Cat., Boston, Op. Cit.). Indeed, amidst Warhol's art there is only one other subject whose character so ethereally defies categorization and who so acutely conflated total fame with the inevitability of mortality. In Warhol's work, only Elvis and Marilyn harness a pictorial magnetism of mythic proportions.
With Marilyn Monroe, whom Warhol depicted immediately after her premature death in August 1962, he discovered a memento mori to unite the obsessions driving his career: glamour, beauty, fame, and death. As a star of the silver screen and the definitive international sex symbol, Marilyn epitomized the unattainable essence of superstardom that Warhol craved. Just as there was no question in 1963, there remains still none today that the male equivalent to Marilyn is Elvis. However, despite his famous 1968 adage, "If you want to know all about Andy Warhol, just look at the surface of my paintings" Warhol's fascination held purpose far beyond mere idolization. As Rainer Crone explained in 1970, Warhol was interested in movie stars above all else because they were "people who could justifiably be seen as the nearest thing to representatives of mass culture." (Rainer Crone, Andy Warhol, New York, 1970, p. 22). Warhol was singularly drawn to the idols of Elvis and Marilyn, as he was to Marlon Brando and Liz Taylor, because he implicitly understood the concurrence between the projection of their image and the projection of their brand. Some years after the present work he wrote, "In the early days of film, fans used to idolize a whole star - they would take one star and love everything about that star...So you should always have a product that's not just 'you.' An actress should count up her plays and movies and a model should count up her photographs and a writer should count up his words and an artist should count up his pictures so you always know exactly what you're worth, and you don't get stuck thinking your product is you and your fame, and your aura." (Andy Warhol, The Philosophy of Andy Warhol (From A to B and Back Again), San Diego, New York and London, 1977, p. 86).
The film stars of the late 1950s and early 1960s that most obsessed Warhol embodied tectonic shifts in wider cultural and societal values. In 1971 John Coplans argued that Warhol was transfixed by the subject of Elvis, and to a lesser degree by Marlon Brando and James Dean, because they were "authentically creative, and not merely products of Hollywood's fantasy or commercialism. All three had originative lives, and therefore are strong personalities; all three raised - at one level or another - important questions as to the quality of life in America and the nature of its freedoms. Implicit in their attitude is a condemnation of society and its ways; they project an image of the necessity for the individual to search for his own future, not passively, but aggressively, with commitment and passion." (John Coplans, "Andy Warhol and Elvis Presley," Studio International, vol. 181, no. 930, February 1971, pp. 51-52). However, while Warhol unquestionably adored these idols as transformative heralds, the suggestion that his paintings of Elvis are uncritical of a generated public image issued for mass consumption fails to appreciate the acuity of his specific re-presentation of the King.
As with Marilyn, Liz and Marlon, Warhol instinctively understood the Elvis brand as an industrialized construct, designed for mass consumption like a Coca-Cola bottle or Campbell's Soup Can, and radically revealed it as a precisely composed non-reality. Of course Elvis offered Warhol the biggest brand of all, and he accentuates this by choosing a manifestly contrived version of Elvis-the-film-star, rather than the raw genius of Elvis as performing Rock n' Roll pioneer. A few months prior to the present work he had silkscreened Elvis' brooding visage in a small cycle of works based on a simple headshot, including Red Elvis, but the absence of context in these works minimizes the critical potency that is so present in Double Elvis. With Double Elvis we are confronted by a figure so familiar to us, yet playing a role relating to violence and death that is entirely at odds with the associations entrenched with the singer's renowned love songs. Although we may think this version of Elvis makes sense, it is the overwhelming power of the totemic cipher of the Elvis legend that means we might not even question why he is pointing a gun rather than a guitar. Thus Warhol interrogates the limits of the popular visual vernacular, posing vital questions of collective perception and cognition in contemporary society.
The notion that this self-determinedly iconic painting shows an artificial paradigm is compounded by Warhol's enlistment of a reflective metallic surface, a treatment he reserved for his most important portraits of Elvis, Marilyn, Marlon and Liz. Here the synthetic chemical silver paint becomes allegory for the manufacture of the Elvis product, and directly anticipates the artist's 1968 statement: "Everything is sort of artificial. I don't know where the artificial stops and the real starts. The artificial fascinates me, the bright and shiny..." (Artist quoted in Exh. Cat., Stockholm, Moderna Museet and traveling, Andy Warhol, 1968, n.p.). At the same time, the shiny silver paint of Double Elvis unquestionably denotes the glamour of the silver screen and the attractive fantasies of cinema. At exactly this time in the summer of 1963 Warhol bought his first movie camera and produced his first films such as Sleep, Kiss and Tarzan and Jane Regained. Although the absence of plot or narrative convention in these movies was a purposely anti-Hollywood gesture, the unattainability of classic movie stardom still held profound allure and resonance for Warhol. He remained a celebrity and film fanatic, and it was exactly this addiction that so qualifies his sensational critique of the industry machinations behind the stars he adored.
Double Elvis was executed less than eighteen months after he had created 32 Campbell's Soup Cans for his immortal show at the Ferus Gallery, Los Angeles in July and August 1962, and which is famously housed in the Museum of Modern Art, New York. In the intervening period he had produced the series Dollar Bills, Coca-Cola Bottles, Suicides, Disasters, and Silver Electric Chairs, all in addition to the portrait cycles of Marilyn and Liz. This explosive outpouring of astonishing artistic invention stands as definitive testament to Warhol's aptitude to seize the most potent images of his time. He recognized that not only the product itself, but also the means of consumption - in this case society's abandoned deification of Elvis - was symptomatic of a new mode of existence. As Heiner Bastian has precisely summated: "the aura of utterly affirmative idolization already stands as a stereotype of a 'consumer-goods style' expression of an American way of life and of the mass-media culture of a nation." (Exh. Cat., Berlin, Neue Nationalgalerie (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 2001, p. 28).
For Warhol, the act of image replication and multiplication anaesthetized the effect of the subject, and while he had undermined the potency of wealth in 200 One Dollar Bills, and cheated the terror of death by electric chair in Silver Disaster # 6, the proliferation of Elvis here emasculates a prefabricated version of character authenticity. Here the cinematic quality of variety within unity is apparent in the degrees to which Presley's arm and gun become less visible to the left of the canvas. The sense of movement is further enhanced by a sense of receding depth as the viewer is presented with the ghost like repetition of the figure in the left of the canvas, a 'jump effect' in the screening process that would be replicated in the multiple Elvis paintings. The seriality of the image heightens the sense of a moving image, displayed for us like the unwinding of a reel of film.
Elvis was central to Warhol's legendary solo exhibition organized by Irving Blum at the Ferus Gallery in the Fall of 1963 - the show having been conceived around the Elvis paintings since at least May of that year. A well-known installation photograph shows the present work prominently presented among the constant reel of canvases, designed to fill the space as a filmic diorama. While the Elvis canvases...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Figurative Paintings
Materials
Enamel
$75,000
H 82 in W 40 in D 1 in
Male Nude from Numbered Nudes Series, multiple exposure signed exhibition print
By Jack Mitchell
Located in Senoia, GA
4625 2 10 1986 1/20. This is a vintage gelatin silver print, selenium toned, made by hand by master photographer Jack Mitchell and signed both on the recto and verso. Chosen by the p...
Category
1980s Pop Art Black and White Photography
Materials
Silver Gelatin
$1,350 Sale Price
43% Off
H 20 in W 24 in
Black and White I, II and III, Expanded Metal Painting. Triptych
Located in Miami Beach, FL
His The panel paintings "Expanded Metal Paintings" are the closest to the classic art of painting. Firstly paint is applied by a brush on a primed canvas. Then wire mesh is dunked in...
Category
2010s Abstract Abstract Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil
$42,000
H 59.06 in W 141.74 in D 0.79 in
Sliced Photo Collage on Black Bristol ONE : photography collage
By Barbara Rosenthal
Located in New York, NY
Barbara Rosenthal’s Conceptual Photography is a concrete manifestation of complex inner stresses from external realities of all kinds: physical, familial, political, religious, time,...
Category
2010s Abstract Mixed Media
Materials
Mixed Media, Board, Giclée
Vintage Silver Gelatin Print Photograph Marcus Leatherdale Shrouded Figure Photo
Located in Surfside, FL
Marcus Leatherdale (1952 - 2022)
Silver gelatin print with copper leaf mount
1987
Titled: High Priest. From the Demigod series.
Hand signed and dated and bears artist studio stamp verso.
Provenance: Greathouse Gallery (with label & information verso)
Edition: 1 of 10.
Dimensions mage measures 12" x 5", total measurements are 24" x 13"
Marcus Leatherdale was a Canadian portrait photographer.
Marcus Andrew Leatherdale was born on 18 September 1952, in Montreal, Canada, to Jack Leatherdale, a veterinarian, and Grace Leatherdale, a homemaker. He attended the San Francisco Art Institute.
Leatherdale arrived in New York City in 1978, where he attended the School of Visual Arts. started his career in New York City during the early eighties, setting up a studio on Grand Street.
Leatherdale first served as Robert Mapplethorpe office manager for a while and was photographed in the nude by the master, grabbing a rope with his right hand and holding a rabbit in his left.
Thereafter he worked as an assistant curator to Sam Wagstaff. He soon became a darling of the then vibrant club scene and the fashionable media: Interview, Details, The New Yorker, Vanity Fair, and Elle Decor presented his work. Later on he was featured in artsy publications as Artforum, Art News, and Art in America. Leatherdale was the Cecil Beaton of downtown New York,
He photographed a not-yet-famous club kid named Madonna in her ripped jeans and his denim vest. The performance artist Leigh Bowery was majestic in a tinseled mask, a corset and a merkin. Andy Warhol was a Hamlet in a black turtleneck. Susanne Bartsch, the nightlife impressaria, was a towering presence in red leather. He documented the New York City lifestyle, the extraordinary people of Danceteria and Club 57 where he staged his first exhibits in 1980. Leatherdale was an acute observer of the New York City of the nineteen eighties. His models were the unknown but exceptional ones – like Larissa, Claudia Summers or Ruby Zebra – or well known artists – like Madonna, Keith Haring, Andy Warhol, Winston Tong and Divine, Trisha Brown, Lisa Lyon, Andrée Putman, Kathy Acker and Sydney Biddle Barrows, otherwise known as the Mayflower Madam, Jodie Foster, and fellow photographer John Dugdale. He Married Claudia Summers, theirs was not a traditional marriage, but they were best friends, and he was Canadian, so it made life easier if they wed. His boyfriend for a time was Robert Mapplethorpe, whose photography studio Mr. Leatherdale also managed. He and Mapplethorpe were a striking pair, dressed like twins in leather and denim, their faces as if painted by Caravaggio, and they often photographed each other.
Jean-Michel Basquiat was often hanging out there, playing his bongo drums; so were friends like Cookie Mueller, the doomed, gimlet-eyed author and Details magazine contributor who was for a time Mapplethorpe’s and Ms. Summers’ drug dealer, and Kathy Acker, the performance artist and novelist. For quite a while Leatherdale remained in Mapplethorpe's shadow, but was soon discovered as a creative force in his own right by Christian Michelides, the founder of Molotov Art Gallery in Vienna. Leatherdale flew to Vienna, presented his work there and was acclaimed by public and press.
This international recognition paved his way to museums and permanent collections such as the Rheinisches Landesmuseum Bonn, the Art Institute of Chicago, the Australian National Gallery in Canberra, the London Museum in London, Ontario, and Austria's Albertina. He was included in the MoMA exhibit New York/New Wave along with Kenny Scharf, William Burroughs, John Crash Matos, Larry Clark, Nan Goldin, Lawrence Weiner and Stephen Sprouse. Above all, his arresting portraits of New York City celebrities in the series Hidden Identities aroused long-lasting interest amongst curators and collectors.
In 1993, Leatherdale began spending half of each year in India's holy city of Banaras. Based in an ancient house in the centre of the old city, he began photographing the diverse and remarkable people there, from the holy men to celebrities, from royalty to tribals, carefully negotiating his way among some of India's most elusive figures to make his portraits. From the outset, his intention was to pay homage to the timeless spirit of India through a highly specific portrayal of its individuals. His pictures include princesses and boatmen, movie stars and circus performers, and street beggars and bishops, mothers and children in traditional garb. Leatherdale explored how essentially unaffected much of the country was by the passage of time; and it has been remarked upon that this approach is distinctly post-colonial. In 1999, Leatherdale relocated to Chotanagpur (Jharkhand) where he focusing upon the Adivasis. Later Serra da Estrela in the mountains of central Portugal became his second home base.
Leatherdale's matte printing techniques, which adapt nineteenth-century processes and employ half black, half sepia colorations, reinforce the timelessness of his subjects. Tones and matte surfaces effectively differentiate his portraits from the easy slickness of fashion photography.
In 2019, Mr. Leatherdale compiled his work from 80s in a book entitled “Out of the Shadows”, written with Claudia Summers.
During his time in New York City, he dated Robert Mapplethorpe, whose photography studio Leatherdale managed. His partner of two decades, Jorge Serio, died in July 2021
Major exhibitions
1980 Urban Women, Club 57, NYC
1980 Danceteria, NYC
1981 Stilvende, NYC
1982 The Clock Tower, PS1, NYC
1982 544 Natoma Gallery, San Francisco
1982 Eiko And Koma, Stilvende, NYC
1983 Form And Function Gallery, Atlanta
1983 Galerie in der GGK Wien, Vienna, Austria
1983 The Ring, Vienna (organized by Molotov)
1983 London Regional Art Gallery, London, Ontario, Canada
1984 Performance, Greathouse Gallery, NYC
1984 Social Segments, Grey Art Gallery, NYU
1984 Rheinisches Landesmuseum, Bonn
1985 Ritual, Greathouse Gallery, NYC
1985 Artinzer, Munich
1985 Leatherdale/Noguchi, Gallery 291, Atlanta
1985 Paul Cava Gallery, Philadelphia
1986 Poison Ivy, Greathouse Gallery, NYC
1986 Wessel O’Connor Gallery, Rome
1986 Hidden Identities, Michael Todd Gallery, Palladium, NYC
1987 Demigods, Greathouse Gallery, NYC
1987 Collier Gallery, Scottsdale, Arizona
1987 Tunnel Gallery, NYC
1988 Claus Runkel Fine Art Ltd., London, UK
1988 Madison Art Center, Madison
1989 Wessel-O’Connor Gallery, NYC
1989 Summer Night Festival, Onikoube, Sendai
1990 Bent Sikkema Fine Art, NYC
1990 Fahey-Klein Gallery, Los Angeles
1990 Faye Gold Gallery, Atlanta
1990 Mayan Theatre, Los Angeles
1991 Runkel Hue-Williams Gallery, London
1991 Galerie Michael Neumann, Düsseldorf
1991 Arthur Rogers Gallery, New Orleans
1992 Arthur Rogers, NYC
1992 Galerie Del Conte, Milwaukee
1993 Galerie Bardamu, NYC
1996 Fayf Gold Gallery, Atlanta
1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 Bridgewater/Lustberg, NYC
1998 Rai Krishna Das...
Category
1980s 85 New Wave Black and White Photography
Materials
Silver Gelatin
Male Nude from Numbered Nudes Series, multiple exposure signed exhibition print
By Jack Mitchell
Located in Senoia, GA
5203 4 41 1995 1/20. This is a vintage gelatin silver print, selenium toned, made by hand by master photographer Jack Mitchell and signed both on the recto and verso. Chosen by the ...
Category
1990s Pop Art Black and White Photography
Materials
Silver Gelatin
$1,350 Sale Price
43% Off
H 20 in W 24 in
Artist Josef Levi with his work, multiple exposure signed by Jack Mitchell
By Jack Mitchell
Located in Senoia, GA
11 x 14" vintage silver gelatin photograph of artist Josef Levi with his work multiple exposure, 1970. Signed on the print verso by Jack Mitchell. Comes directly from the Jack Mitch...
Category
1970s Pop Art Black and White Photography
Materials
Silver Gelatin
$1,350 Sale Price
20% Off
H 11 in W 14 in D 0.03 in
Large format vintage multiple exposure male nude, signed by Jack Mitchell
By Jack Mitchell
Located in Senoia, GA
16 x 20" vintage silver gelatin photograph, multiple exposure male nude. Titled, numbered, dated, and signed by Jack Mitchell on the recto. Comes directly from the Jack Mitchell Arch...
Category
1990s Abstract Black and White Photography
Materials
Silver Gelatin
$900 Sale Price
40% Off
H 20 in W 16 in
"Elvis Army Mugshot" Print on canvas 39 x 36 inch Ed. of 75 by Gerard Marti
By Gerard Marti
Located in Culver City, CA
"Elvis Army Mugshot" Print on canvas 39 x 36 inch Ed. of 75 by Gerard Marti
Giclee print on canvas
Stretched on wooden bars.
Signed and numbered by the artist.
Although this photo is commonly referred to as Elvis Presley’s “mugshot”, this photo of Elvis...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Portrait Prints
Materials
Canvas, Digital
$2,850
H 39 in W 36 in D 1.5 in
More From This Seller
View All84x48 "Triple Elvis by Warhol" Photomosaic Pop Fine Art Photography Signed
By Destro
Located in Los Angeles, CA
"TRIPLE ELVIS BY ANDY WARHOL" is a photomosaic artwork by Destro.
Destro has created large prints which are made up of many hundreds of smaller images.
Archival photographic paper ...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary American Modern Black and White Photography
Materials
Archival Pigment
64x48 "Triple Elvis by Warhol" Photomosaic Pop Fine Art Photography
By Destro
Located in Los Angeles, CA
"TRIPLE ELVIS BY ANDY WARHOL" is a photomosaic artwork by Destro.
Destro has created large prints which are made up of many hundreds of smaller images.
Archival photographic paper ...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary American Modern Black and White Photography
Materials
Archival Pigment
$1,160 Sale Price
20% Off
64x48" Elvis by Warhol" Photomosaic Pop Fine Art Photography Signed
By Destro
Located in Los Angeles, CA
"ELVIS BY ANDY WARHOL" is a photomosaic artwork by Destro.
Destro has created large prints which are made up of many hundreds of smaller images.
Archival photographic paper
Editio...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary American Modern Black and White Photography
Materials
Archival Pigment
$1,240 Sale Price
20% Off
64x48" Elvis by Warhol" Photomosaic Pop Fine Art Photography
By Destro
Located in Los Angeles, CA
"ELVIS BY ANDY WARHOL" is a photomosaic artwork by Destro.
Destro has created large prints which are made up of many hundreds of smaller images.
Archival photographic paper
Framin...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary American Modern Black and White Photography
Materials
Archival Pigment
50x40" Elvis by Warhol" Photomosaic Pop Fine Art Photography Unsigned Print
By Destro
Located in Los Angeles, CA
"ELVIS BY ANDY WARHOL" is a photomosaic artwork by Destro.
Destro has created large prints which are made up of many hundreds of smaller images.
Archival photographic paper
Framin...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary American Modern Black and White Photography
Materials
Archival Pigment
$400 Sale Price
20% Off
Elvis Presley Andy Warhol 20x10 Photomosaic Photography Aluminum Metal Pop Art
By Destro
Located in Los Angeles, CA
"Elvis by Warhol " is an acrylic photomosaic artwork by Destro. The first release in a series mosaic works called "Icons". Destro has created large prints which are made up of many ...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary American Modern Black and White Photography
Materials
Archival Pigment