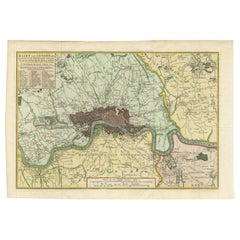
The map of Batavia (modern-day Jakarta) from 1681, attributed to Frederick de Wit holds significant historical importance for several reasons:
Historical Context
1. Colonial Era: This map dates back to the Dutch colonial era when Batavia served as the administrative and commercial hub of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). The VOC was a powerful trading entity that played a crucial role in the global spice trade and colonization in Southeast Asia.
2. Strategic Importance: Batavia was strategically located on the northwestern coast of Java, providing the Dutch with a critical base for their maritime operations. The city became the center of Dutch political and military control in the region.
Cartographic Significance
1. Detailed Urban Layout: The map meticulously details the layout of Batavia, including its fortifications, canals, streets, and significant buildings. This level of detail provides insights into the urban planning and architectural styles of the period.
2. Military Engineering: The fortifications shown on the map illustrate the advanced military engineering techniques used by the Dutch to protect their valuable colony. The walls, bastions, and moats indicate the strategic considerations taken to defend against potential invasions.
3. Maritime Activity: The depiction of ships in the harbor highlights Batavia's role as a major maritime center. The VOC's fleets were essential for trade routes connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia, making Batavia a crucial node in global commerce.
Artistic and Cultural Value
1. Artistic Elements: The decorative elements, such as the lion holding a shield and the intricate cartouches, reflect the artistic trends of Dutch Golden Age cartography. These embellishments were not only informative but also served to display the cartographer's skill and the map's prestige.
2. Cultural Exchange: Maps like this one provide evidence of cultural exchange between the Dutch and the indigenous populations of Java. The blending of Dutch and local influences can be seen in various aspects of the map and the architecture of the city.
Rarity and Preservation
1. Rarity: Maps from the 17th century, especially those in good condition, are relatively rare and highly valued by collectors and historians. Each map provides a unique snapshot of historical geography and urban development.
2. Preservation of History: This map serves as a historical document, preserving knowledge about Batavia's cityscape, infrastructure, and colonial governance. It helps historians and scholars understand the socio-economic and political dynamics of the period.
Conclusion
The map of Batavia from 1681 is special due to its detailed depiction of one of the most important colonial cities in Southeast Asia during the Dutch Golden Age. It reflects the strategic, economic, and cultural significance of Batavia, serving as a valuable resource for understanding the history of Dutch colonialism and its global impact. The map's artistry and precision make it an important artifact in the history of cartography.
---------------
The map is an original and historical map of Batavia (present-day Jakarta) on the island of Java, dated 1681. There are several details to consider when evaluating its origins and possible authorship:
1. **Style and Detail**: The intricate details and style are reminiscent of maps created by Frederick de Wit, a prominent Dutch cartographer and engraver of the 17th century. He was known for his detailed city maps and sea charts.
2. **Lack of Signature**: The absence of "F. de Wit, Excudit" could indicate either an omission or a different engraver. However, it is essential to note that some maps from that period were reproduced or copied by other engravers and cartographers. This was not uncommon, as map-making was a collaborative effort, and copies of popular maps were frequently made.
3. **Map Characteristics**:
- The depiction of ships and the detailed fortifications are typical of Dutch cartography in the late 17th century.
- The decorative elements, such as the lion holding a shield, are also characteristic of Dutch map engravers.
4. **Other Possible Engravers**: While Frederick de Wit is a strong candidate, other notable Dutch engravers from that period include Joan Blaeu and Willem Janszoon Blaeu. They also produced highly detailed maps and could potentially be the creators or inspirers of this map.
To determine the precise authorship, you might consider:
- **Comparing** this map with other confirmed works of Frederick de Wit and his contemporaries to identify stylistic similarities and differences.
- **Historical Records**: Consulting historical records or publications related to Dutch cartography in the 17th century might provide more context or even direct references to this particular map.
If you have access to additional details or higher-resolution images of specific sections, it might help further pinpoint the map's origin and authorship.
-------------
Frederick de Wit (1629–1706) was a prominent Dutch cartographer, engraver, and publisher known for his detailed and decorative maps, atlases, and globes. He played a significant role in the Dutch Golden Age of cartography, contributing to the wealth of geographic knowledge and artistic achievement during this period. Here are key aspects of his life and work:
### Biography
- **Early Life**: Frederick de Wit was born in Gouda, Netherlands, in 1629. Little is known about his early years, but he moved to Amsterdam, the epicenter of Dutch cartography, in the mid-17th century.
- **Career Beginnings**: De Wit began his career as an engraver and publisher, initially producing maps that were reissues of earlier works by other cartographers, such as Joan Blaeu and Willem Janszoon Blaeu.
### Contributions to Cartography
- **Mapmaking**: De Wit was known for his meticulous attention to detail and artistic flair. He produced a wide range of maps, including world maps, regional maps, city plans, and
maritime charts...